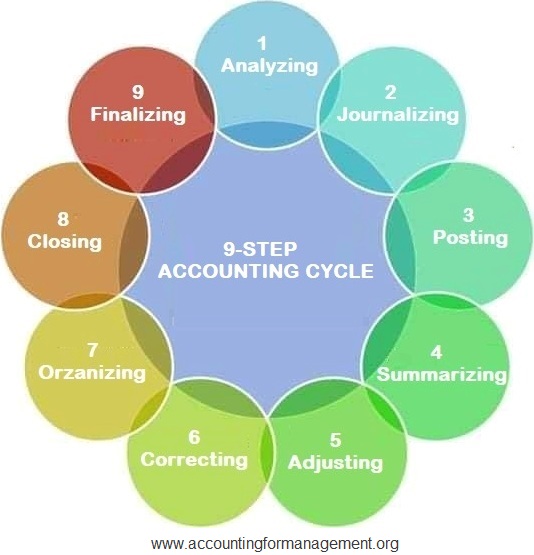
Maintaining a consistent accounting cycle will help you notice balance discrepancies at a glance. The accounting cycle is a standard, 8-step process that tracks, records, and analyzes all financial activity and transactions within a business. It starts when a transaction is made and ends when a financial statement is issued and the books are closed. An accounting process records a company’s financial transactions for an accounting period to provide accurate details to the internal and external stakeholders.
Are bookkeeping and accounting different?
However, the following process for tracking activity and creating financial statements doesn’t change. The first step of the accounting process is the analysis of the transactions. First, the accountants collect, identify, and classify receipts, invoices, and other financial data.
Step 6: Adjust Journal Entries
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. During the month of January, Haram’s Company process the following transactions.
Book a demo with our friendly team of experts
To be a successful forensic accountant, one must be detailed, organized, and naturally inquisitive. This position will need to retrace the steps a suspect may have taken to cover up fraudulent financial activities. Understanding how a company operates can help identify fraudulent activities that veer from the company’s position.
Its format is similar to that of an unadjusted and adjusted trial balance. However, it lists only permanent accounts because all temporary accounts get closed in step 8 above. The post-closing trial balance serves as the base or opening trial balance for the next period’s accounting cycle. Posting is the process of forwarding journal entries from journal book to ledger book, commonly known as general ledger. After journalizing, the accounting transactions are posted to their relevant ledger accounts. This step classifies and groups all entries relating to a particular account in one place.
- Once the adjusted trial balance is complete, create your financial statement or annual report.
- Barbara has an MBA from The University of Texas and an active CPA license.
- When you record all transactions in the general journal, now, is the time to post these all transactions in the appropriate T account (General Ledger).
- Business.com aims to help business owners make informed decisions to support and grow their companies.
- Even if you hire a CPA or get a bookkeeper to oversee your accounting cycle, accounting software can simplify their duties.
steps of the accounting cycle
A worksheet is where you adjust the “unadjusted” trial balance if needed. If the trial balance reveals errors, the worksheet can help identify the reason for it. Accruals have to do with revenues you weren’t immediately paid for and expenses you didn’t immediately pay. Think of the unpaid bill that you sent to the customer two weeks ago, or the invoice from your supplier you haven’t sent money for. If you use accounting software, this usually means you’ve made a mistake inputting information into the system.
For example, a personal loan made by a business owner that does not have anything to do with the business shall not be recorded in the books of the business. When the owner buy a personal car, it should also not be recorded as an asset of the business. Always watch for the separation of personal and business transactions. An example of an adjustment is a salary or bill paid later in the accounting period. Because it was recorded as accounts payable when the cost originally occurred, it requires an adjustment to remove the charge.
Computerized accounting systems and the uniform process of the accounting cycle have helped to reduce mathematical errors. This process is repeated for all revenue and expense ledger accounts. Balance sheet accounts (such as bank accounts, credit cards, etc.) do not need closing 4 popular free and open source accounting software entries as their balances carry over. The last step in the accounting cycle is preparing financial statements—they’ll tell you where your money is and how it got there. It’s probably the biggest reason we go through all the trouble of the first five accounting cycle steps.
These statements explain a company’s financial standing and serve as indicators of operational performance. Note that some steps are repeated more than once during a period. Obviously, business transactions occur and numerous journal entries are recording during one period.
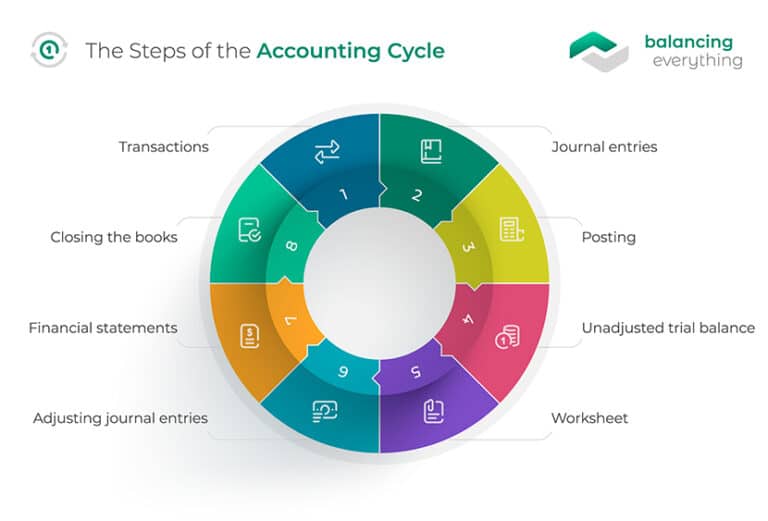
The accounting cycle is a multi-step process designed to convert all of your company’s raw financial information into financial statements. The accounting cycle is a series of eight steps that a business uses to identify, analyze, and record transactions and the company’s accounting procedures. If the total credit and debit balances don’t match, you need to figure out what’s missing, record those transactions and post these adjusting entries to the general ledger. The accounting cycle incorporates all the accounts, journal entries, T accounts, debits, and credits, adjusting entries over a full cycle. Accounting software saves time and effort by automating the entire accounting cycle. As your business grows, you may find you need more than one person to handle the accounting cycle steps for your company.
It is a standard 8-step process that begins when a transaction occurs and ends with its inclusion in the financial statements and the closing of the books. The final step is to document the post-closing trial balance to review debits and credits before the next accounting period begins. Because this step zeroes out your revenue, the post-closing trial balance would only include balance sheet accounts. The accounting cycle involves all of the financial transactions for a business. It refers to recording these transactions, as well as processing them. This includes when a financial transaction occurs, all the way to the creation of financial statements.